The World Happiness Report offers key insights into global happiness trends. It highlights the correlation between happiness and life satisfaction. Research found that people with higher life satisfaction are generally happier. This blog explores happiness across life events, income, and why reliving memories boosts joy.
Key Takeaways
Overview of Happiness Statistics in 2024
General Happiness Statistics
- Happiness Peak Age: People report feeling happiest between the ages of 30 to 34 years old.
- Millennials’ Happiness: In a survey, 57% of millennials (ages 25-40) reported being the happiest generation.
- Generational Happiness: Generation X (ages 41-56) reported a happiness level of 52%, while Baby Boomers and Generation Z (ages 18-24) both rated their happiness at 41%.
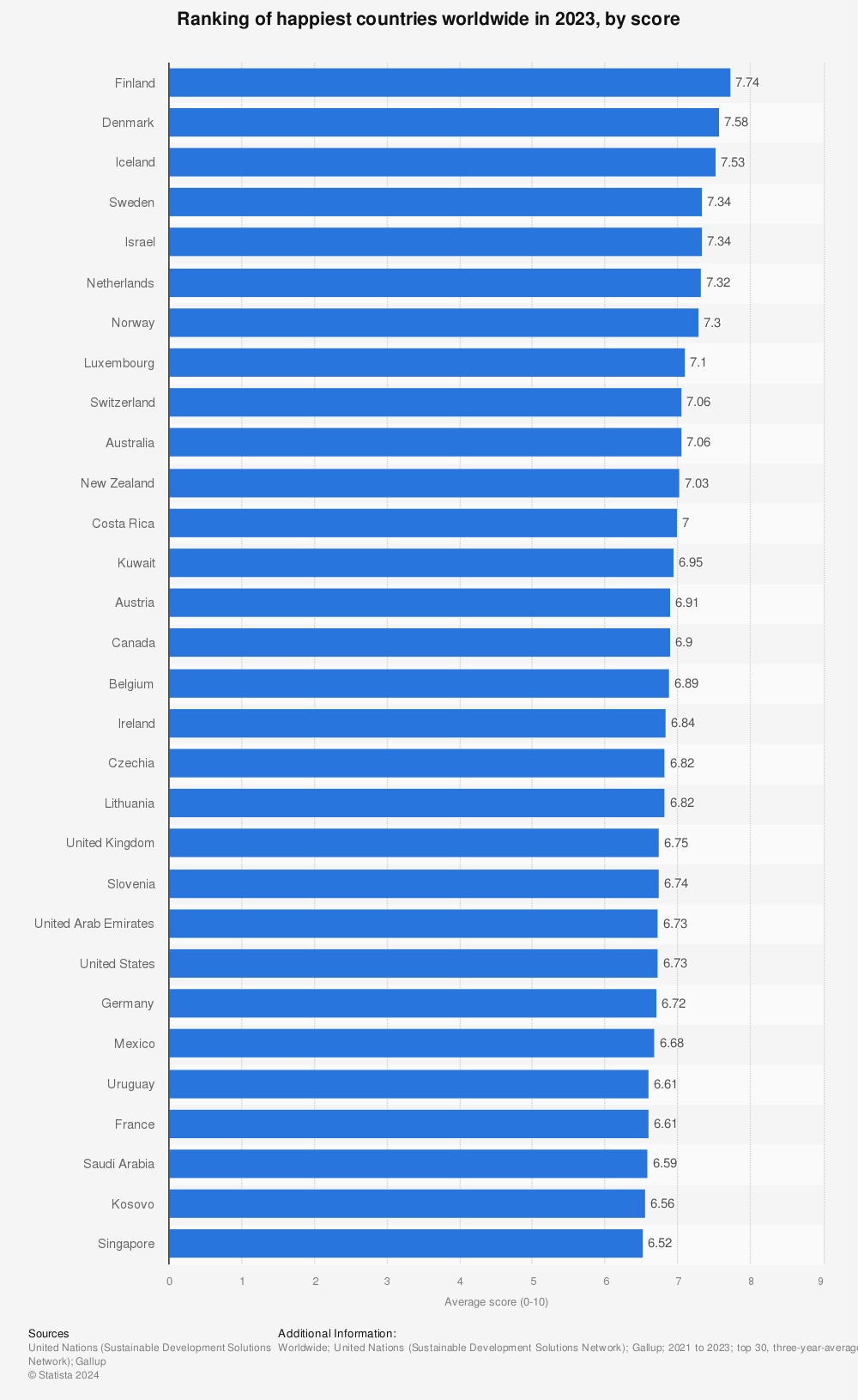
- Global Happiness Rankings: Finland has consistently ranked as the happiest country in the world for seven consecutive years, followed by Denmark and Switzerland.
- Young People’s Decline: Young people’s happiness is declining in the West, with the U.S. dropping out of the top 20 happiest countries for the first time.
- Happiness Income Paradox: Personal income significantly impacts emotional well-being, but life satisfaction levels plateau after reaching certain income levels.
- Happiness and Health: Happiness is positively correlated with health, influencing life satisfaction and mental well-being across all ecological and social systems.
- Older Adults’ Happiness: In China, older adults report higher satisfaction with life compared to younger individuals.
- Social Relationships: Across all generations, relationships with others are frequently cited as essential to happiness.
Age and Gender Insights
- Young Women’s Happiness: Globally, young women report being the happiest demographic group, although the difference is narrow.
- Older Generations’ Satisfaction: Individuals born before 1965 tend to be happier than those born after 1980, with this gap widening as they age.
- Happiness by Age Group: For those under 30, happiness levels are now equal in both Western and Eastern Europe.
Economic Factors
- Income Thresholds: Research indicates that happiness increases with income up to $75,000 annually; beyond this point, the increase in happiness diminishes significantly.
- High Income Impact: A new study suggests that for most people, happiness can continue to rise with income up to $500,000 per year.
- Employment and Happiness: Employment is a significant determinant of happiness worldwide; happier individuals are more likely to vote and support incumbents.
Lifestyle and Well-being
- Physical Activity Correlation: Engaging in light to moderate physical activity is linked to higher levels of happiness.
- Dietary Choices: Healthier dietary choices, such as increased fruit and vegetable consumption, are associated with greater happiness levels.
- Mental Health Connection: Mental health issues can negatively impact overall happiness and life satisfaction.
Regional Differences
- Top Countries for Older Adults’ Happiness: Denmark ranks highest for happiness among individuals aged 60 and above, followed by other Nordic countries.
- Happiness in Eastern Europe: Central and Eastern European countries have seen significant increases in happiness across all age groups recently.
Psychological Aspects
- Life Evaluation Methodology: The World Happiness Report uses a “Cantril ladder” method where respondents rate their current life on a scale from 0 to 10.
- Positive Emotions Measurement: Positive emotions are measured by responses regarding laughter, enjoyment, and interest in daily activities.
Trends Over Time
- Longitudinal Decline in Happiness: There has been a notable decline in happiness among young people in North America and Western Europe since 2006-2010 compared to recent years.
- Crisis Among Youth: Young people under 30 are experiencing dissatisfaction similar to a mid-life crisis in various parts of the world.
Additional Insights
- Trust Factor: Societal trust and work-life balance contribute significantly to national happiness levels. Finland exemplifies this with its high rankings due to societal structures supporting well-being.
- Happiness vs. Wealth Perception: The perception that money can buy happiness is complex. While it does improve emotional well-being initially, its effects can plateau or diminish over time.
Conclusion
- Cultural Influences on Happiness: Cultural factors play a critical role in shaping individual perceptions of happiness across different regions and demographics.
- Social Support Importance: Satisfaction with social support networks is crucial for maintaining high levels of happiness among younger populations in developed countries.
- Long-term Trends in Happiness Measurement: The methodology for measuring happiness has evolved over time, emphasizing subjective well-being through various indicators including emotional states and life evaluations.
- Global Context of Happiness Trends: The global landscape of happiness is continually shifting due to economic changes, social dynamics, and cultural shifts impacting different age groups differently across regions.
The Link Between Happiness and Life Satisfaction. What Affects Happiness?
Happy people tend to report higher life satisfaction.
Several studies, including the Gallup World Poll, show a strong relationship between happiness and life satisfaction. The Pew Research Center found that happiness tends to fluctuate based on life circumstances. Gallup and Harvard research revealed that health and happiness are closely connected. Personal connections play a role in keeping people happy throughout life.
Key factors affecting happiness:
- Good health
- Strong personal connections
- Income stability
According to a General Social Survey, happy people report being very happy more consistently over time.

Happiness Across Different Life Events
Happiness fluctuates across different life events and stages. The Harvard Study of Adult Development found that people are happier when they maintain strong connections. A longitudinal study showed that people grow happier as they grow older, but the happiness gap between unmarried people and married individuals can widen.
Key findings:
- Self-reported happiness increases with the level of satisfaction in life.
- Healthy and happy individuals report the best possible life experiences.
- Happiness scores tend to rise when people grow stronger personal connections.
A survey conducted on social media use found that less engagement made people happier.
The Correlation Between Income and Happiness
The relationship between income and happiness is complex. Research on happiness shows that per capita income is associated with higher levels of life satisfaction, but beyond a certain point, the impact fades. Nationally representative surveys found that people happy throughout their lives often focus more on relationships than wealth.
Key insights:
- People with higher incomes report being pretty happy, but happiness over time varies.
- Personality traits also play a role in how individuals find happiness.
- Countries with the highest incomes don’t always have the happiest people.

Key Factors That Affect Our Happiness and Life Satisfaction
Several factors impact happiness and life satisfaction. The definition of happiness varies across different sources, but key elements remain consistent. Healthy and happy lives are strongly tied to personal connections, happiness and mental well-being, and income stability. The Harvard Study, one of the world’s longest, found that as people grow older, relationships become more important than wealth.
Can Money Buy Happiness? What Makes People Happiest?
The answer isn’t straightforward. Studies show that income increases average happiness, but only to a point. Beyond that, people are less happy if they rely solely on wealth. Older people often find fulfilment in relationships, not money. According to one of the world’s longest studies of adult life, what makes people happy changes with each stage of life.
Key insights:
- Money can improve happiness, but personal connections bring lasting joy.
- People are likely to report feeling rather happy with balanced lives, not just wealth.
The Role of Higher Income in Happiness Levels
Higher-income plays a role in happiness and life satisfaction among individuals, but only up to a point. Would you say income alone guarantees happiness? Studies suggest otherwise. The pursuit of happiness involves more than wealth, as differences in subjective well-being highlight.
Percentage points of happiness increase with income, but relationships and health still matter most. According to the director of the study, people with strong connections avoid feeling isolated, even in the worst possible life situations.
Why People Who Say They Are Happy Relive Positive Memories
People who say they are happy often relive positive memories to boost their mood. Research shows that revisiting joyful moments helps prevent feelings of isolation. In country characteristics similar to the US, strong personal connections keep us happy and grounded. A report is produced every year, confirming the link between reliving memories and long-term happiness.
Using Klokbox to Capture and Relive Happiness
Klokbox makes it easy to capture and relive your happiest memories. In a world where it’s easy to get isolated, revisiting joyful moments strengthens connections and boosts well-being. With Klokbox, you can organize your memories and share them with loved ones, keeping happiness alive. Reliving these memories helps maintain a positive outlook on life.




